Figures of merit
In direct methods
of solving crystal structures, figures of merit are a measure of the quality
of a given phase set. They indicate how good the phase set is satisfying
the Sayre equation or the tangent formula. The following are figures of
merit used in the direct-method program MULTAN (Main,
Fiske, Hull, Lessinger, Germain, Declercq and Woolfson, 1980) and in
VEC.
1.
The absolute figure of merit:
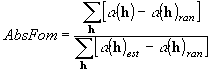 ,
,
where
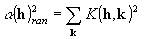 ,
,
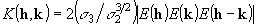 ,
,
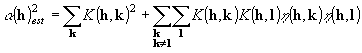 ,
,
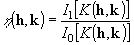 ,
,
I1 and I0 are respectively
the first and zero order modified Bessel functions. AbsFom will
tend to be unity for phases giving the expected values of
a(h)
and zero for random phases. In practice a good set of phases may give AbsFom
in the range 1.0-1.4 for X-ray diffraction data.
2.
The Psi-zero figure of merit:
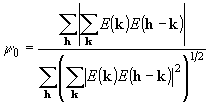 ,
,
where the summation over k is for the large structure
factors, whose phases are being determined, while the summation over h
includes
only small, ideally zero, structure factors, their phases are not known
and not to be determined. The yo
figure of merit is expected to be small for a correct set of phases and
also for a set of random phases. However, a set of phases resulting from
tangent-formula iteration can hardly be randomly distributed. Hence a small
yo
figure of merit usually indicates a good phase set.
3.
The residual figure of merit:
 .
.
Again, a small value of Ra
indicates a good phase set.
4.
The combined figure of merit:
With the three
figures of merit available for a number of different phase sets it is possible
to rank them by a combined figure of merit:
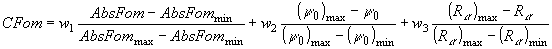 .
.
where w1, w2 and
w3
are
weight factors for the three figures of merit. They are 0.6, 1.2, and 1.2
in the program MULTAN and 0.2, 1.4 and 1.4 in the program
VEC.
The subscripts max refers to the phase set with the greatest value
of figure of merit, while min refers to that with the least value
of figure of merit. A set of phases with best value for each of the figures
of merit would have CFom = 3.0, with the worst value for each then
CFom
= 0.0.
References
Main,
P., Fiske, S.J., Hull, S.E., Lessinger, L., Germain, G., Declercq, J.P.
and Woolfson, M.M. (1980).
MULTAN-80: A System of Computer
Programs for the Automatic Solution of Crystal Structures from X-ray Diffraction
Data. Univs. of York, England and Louvain, Belgium.
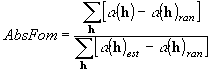 ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
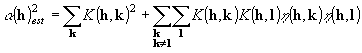 ,
,
![]() ,
,
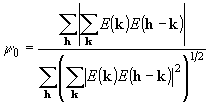 ,
,
 .
.